what causes a firms sales to increase or decrease
Price elasticity of need (PED) shows the relationship between price and quantity demanded and provides a precise calculation of the event of a change in price on quantity demanded.
The following equation enables PED to exist calculated.
We can apply this equation to calculate the effect of price changes on quantity demanded, and on therevenue received by firms before and later any price change.
For case, if the price of a daily newspaper increases from £1.00 to £i.20p, and the daily sales falls from 500,000 to 250,000, the PED will exist:
The negative sign indicates that P and Q are inversely related, which we would expect for most toll/demand relationships. This is meaning because the paper supplier can calculate or estimate how acquirement will be affected by this alter in price. In this instance, revenue at £1.00 is £500,000 (£1 10 500,000) simply falls to £300,000 after the price rise (£1.20 x 250,000).
The range of responses
The degree of response of quantity demanded to a alter in cost can vary considerably. The key criterion for measuring elasticity is whether the co-efficient is greater or less than proportionate. If quantity demanded changes proportionately, then the value of PED is 1, which is called 'unit elasticity'.
PED can as well exist:
-
Less than one, which means PED is inelastic.
-
Greater than one, which is elastic .
-
Zero (0), which is perfectly inelastic .
-
Infinite (∞), which is perfectly elastic .
PED along a linear demand curve
PED on a linear demand curve will fall continuously as the curve slopes downwards, moving from left to right. PED = 1 at the midpoint of a linear demand curve.
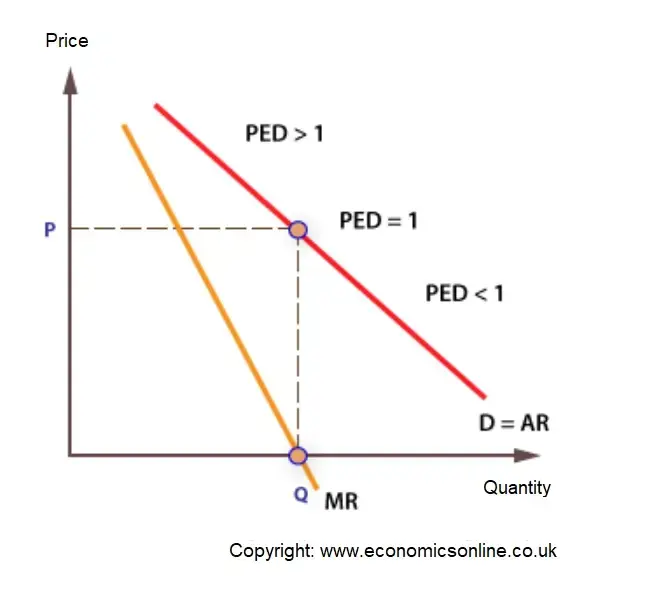
PED and acquirement
In that location is a precise mathematical connection between PED and a business firm'south revenue.
Revenue is measured in threee ways:
-
Total revenue (TR), which is constitute by multiplying price by quantity sold (P x Q).
-
Boilerplate revenue (AR), which is found by dividing total revenue past quantity sold (TR/Q). Average revenue is too the revenue per unit sold, which is likewise the price.
-
Marginal acquirement (MR), which is divers equally the revenue from selling one actress unit. This is calculated by finding the modify in TR from selling one more unit.
Consider these figures and calculate Total, Marginal and Average Revenue.
PRICE
(£)Qd TR MR AR 10 one 9 ii 8 iii 7 iv half dozen 5 5 6 iv vii 3 8 2 9 1 x
Reply
Study the patterns of numbers and see if you can analyse the relationships between the three measures of revenue – and so answer the post-obit:
-
How are price and boilerplate revenue connected?
-
What happens to total revenue as output increases?
-
What is the connection between full acquirement and marginal acquirement?
-
How are marginal acquirement and average revenue connected?
Observations
When TR is at a maximum, MR = zero, and PED = ane
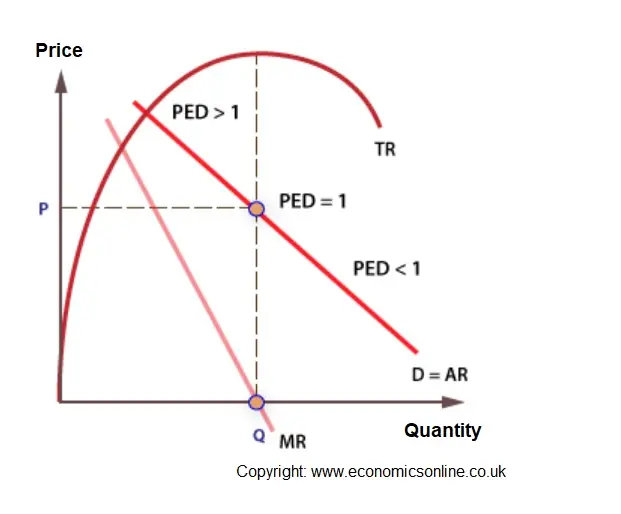
- Price and AR are identical, because AR = TR/Q, which is P x Q/Q, and cancel out the Qs to become P.
- A curve plotting AR (=P) against Q is besides a business firm's need curve.
- TR increases, reaches a peak and decreases.
Why does a firm desire to know PED?
In that location are several reasons why firms gather information about the PED of its products. A business firm will know much more than well-nigh its internal operations and product costs than it will nigh its external surroundings. Therefore, gathering data on how consumers answer to changes in cost can assistance reduce hazard and uncertainly. More specifically, knowledge of PED can assistance the firm forecast its sales and set up its price.
Sales forecasting
The house tin can forecast the touch on of a alter in cost on its sales book, and sales revenue (total revenue, TR). For example, if PED for a product is (-) 2, a x% reduction in price (say, from £10 to £9) will lead to a 20% increase in sales (say from 1000 to 1200). In this case, acquirement will rise from £x,000 to £10,800.
Pricing policy
Knowing PED helps the firm decide whether to enhance or lower price, or whether to price discriminate. Price discrimination is a policy of charging consumers different prices for the same product. If demand is elastic, revenue is gained past reducing price, simply if demand is inelastic, revenue is gained by raising cost.
Non-pricing policy
When PED is highly elastic, the business firm can use advertising and other promotional techniques to reduce elasticity.
Determinants of PED
At that place are several reasons why consumers may respond elastically or inelastically to a price change, including:
The number and 'closeness' of substitutes
A unique and desirable product is likely to showroom an inelastic need with respect to price.
The degree of necessity of the adept
A necessity like breadstuff volition be demanded inelastically with respect to price.
Whether the practiced is addiction forming
Consumers are besides relatively insensitive to changes in the price of habitually demanded products.
The proportion of consumer income which is spent on the good
The PED for a daily newspaper is likely to be much lower than that for a new machine!
Whether consumers are loyal to the brand
Brand loyalty reduces sensitivity to price changes and reduces PED.
Life bicycle of product
PED volition vary co-ordinate to where the product is in its life bicycle. When new products are launched, there are frequently very few competitors and PED is relatively inelastic. As other firms
launch similar products, the wider option increases PED. Finally, equally a product begins to turn down in its lifecycle, consumers can become very responsive to cost, hence discounting is extremely common.
Test your cognition with a quiz
Press Next to launch the quiz
You lot are allowed 2 attempts – feedback is provided afterwards each question is attempted.
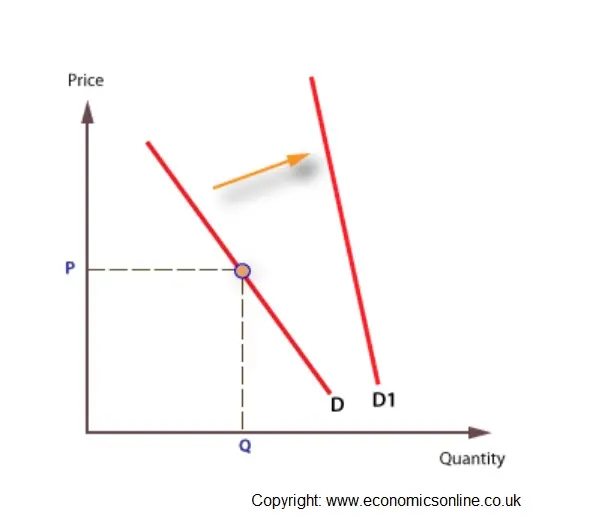
The effects of advertising
Firms may use persuasive advertising by to win new customers and retain the loyalty of existing ones.
Advertisers use a range of media, including television set, press, and electronic media. Advertizement will shift demand to the right, and make need less elastic.
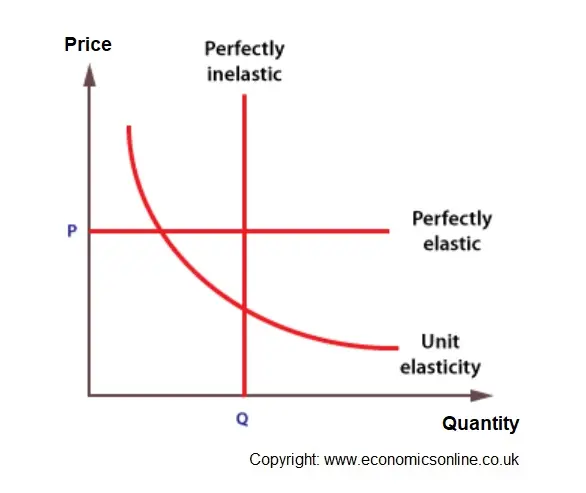
At that place are iii extreme cases of PED.
-
Perfectly elastic , where only i price can exist charged.
-
Perfectly inelastic, where simply 1 quantity volition be purchased.
-
Unit elasticity , where all the possible price and quantity combinations are of the aforementioned value. The resultant bend is called a rectangular hyperbola.
Get to: betoken elasticity of need
PED can likewise be illustrated through indifference curve analysis
Source: https://www.economicsonline.co.uk/competitive_markets/price_elasticity_of_demand.html/
0 Response to "what causes a firms sales to increase or decrease"
Publicar un comentario